
Increasing functional and non-functional requirements in automotive electric/electronic vehicle development will significantly enhance the integration of novel functions in the embedded networks. Major driving forces are the demand for driver assistance function, active and passive safety systems and the fulfillment of environmental and legal requirements. The paper demonstrates that this task in system design can only be managed if the noncompetitive elements are developed together in automotive industry leading to an infrastructure standard like AUTOSAR, FlexRay and LIN. Working on such a basis the OEM can have a dedicated system design environment for the competitive implementations of functions already starting in early phases for feasibility studies. This basis is consequently a fix point through serial development and even in the maintenance phase and enables shared functional development and exploitation as well as in project adaptations of non-automotive industry driven hardware developments.
RELATED VIDEO



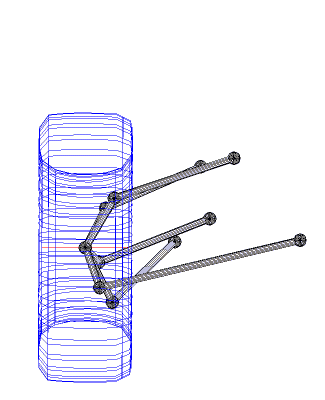 A multi-link suspension is a type of vehicle suspension design typically used in independent suspensions, using three or more lateral arms, and one or more longitudinal arms. A wider definition considers any independent suspensions having 3 control arms or more...
A multi-link suspension is a type of vehicle suspension design typically used in independent suspensions, using three or more lateral arms, and one or more longitudinal arms. A wider definition considers any independent suspensions having 3 control arms or more...
 Air suspension is a type of vehicle suspension powered by an electric or engine driven air pump or compressor. This pump pressurizes the air, using compressed air as a spring. Air suspension is often used in place of conventional steel springs, and in heavy vehicle...
Air suspension is a type of vehicle suspension powered by an electric or engine driven air pump or compressor. This pump pressurizes the air, using compressed air as a spring. Air suspension is often used in place of conventional steel springs, and in heavy vehicle...
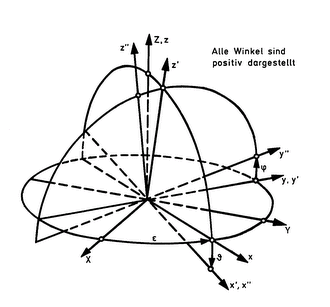 Vehicle dynamics refers to the dynamics of vehicles, here assumed to be ground vehicles. Vehicle dynamics is a part of engineering primarily based on classical mechanics but it may also involve chemistry, solid state physics, electrical engineering, communications...
Vehicle dynamics refers to the dynamics of vehicles, here assumed to be ground vehicles. Vehicle dynamics is a part of engineering primarily based on classical mechanics but it may also involve chemistry, solid state physics, electrical engineering, communications...








